The Rise of the Intelligent Agent
In 2025, the age of artificial intelligence has matured beyond static chatbots and predictive algorithms. We now inhabit a world where AI agents—intelligent, goal-oriented software entities—are not only a part of daily digital experiences but are also transforming how we work, communicate, and innovate. From autonomous task execution to real-time decision-making, AI agents represent a paradigm shift in how technology interacts with the world.
This article explores the evolution, applications, and future implications of AI agents in 2025, offering insights into how they are revolutionizing industries, enhancing human potential, and redefining automation.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are autonomous programs capable of perceiving their environment, making decisions, and executing tasks to achieve specific goals. They combine machine learning, natural language processing, and often, multi-agent systems to perform complex activities independently or collaboratively.
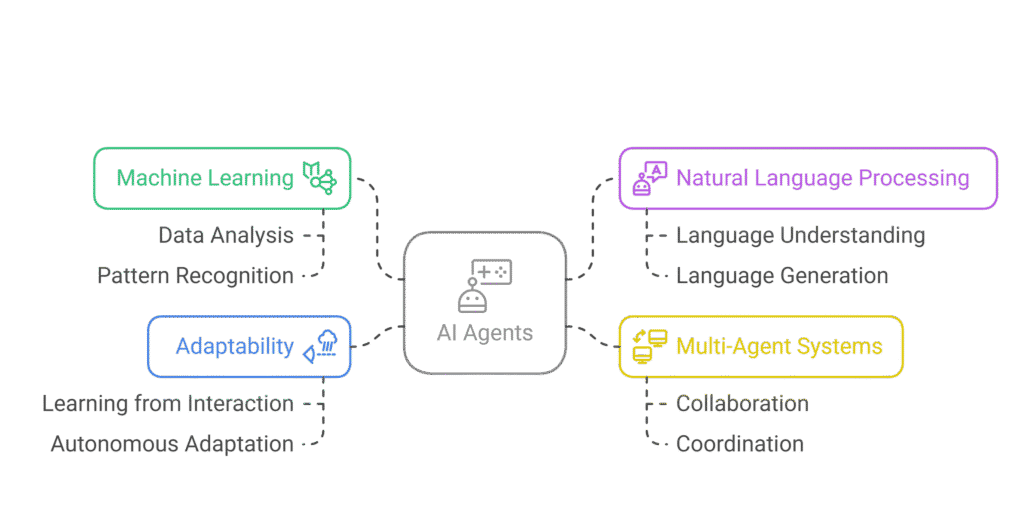
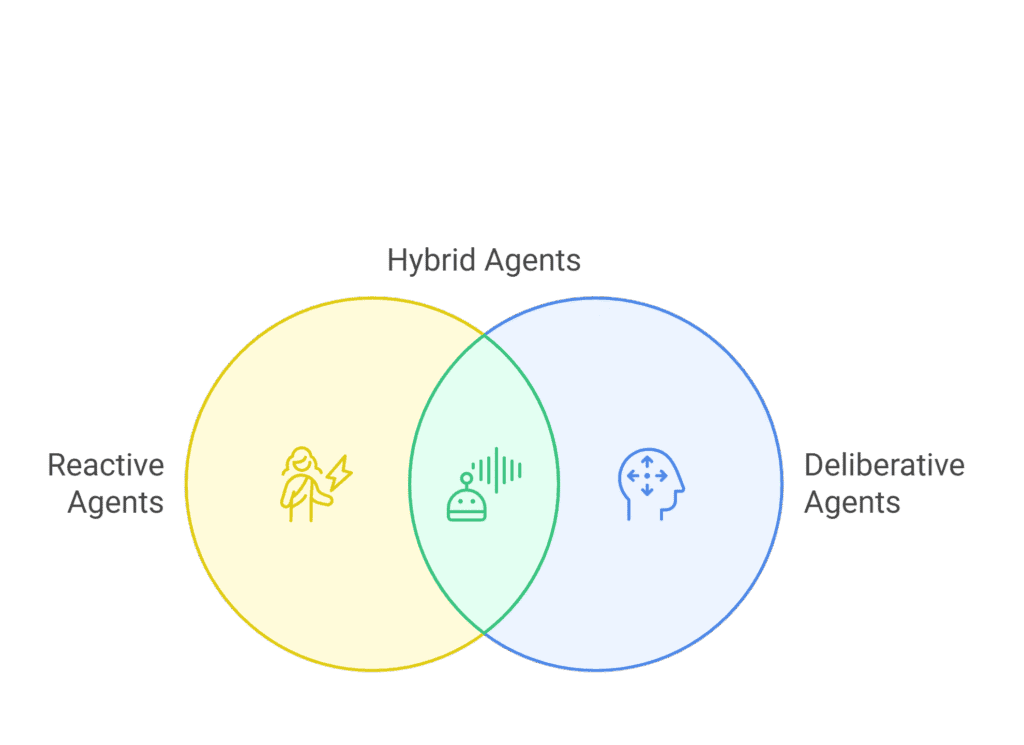
Unlike traditional software, AI agents learn from interaction and can adapt to new conditions without direct human intervention. They can be:
- Reactive Agents: Respond immediately to changes in the environment.
- Deliberative Agents: Use internal models to plan and reason.
- Hybrid Agents: Combine both reactive and deliberative approaches.
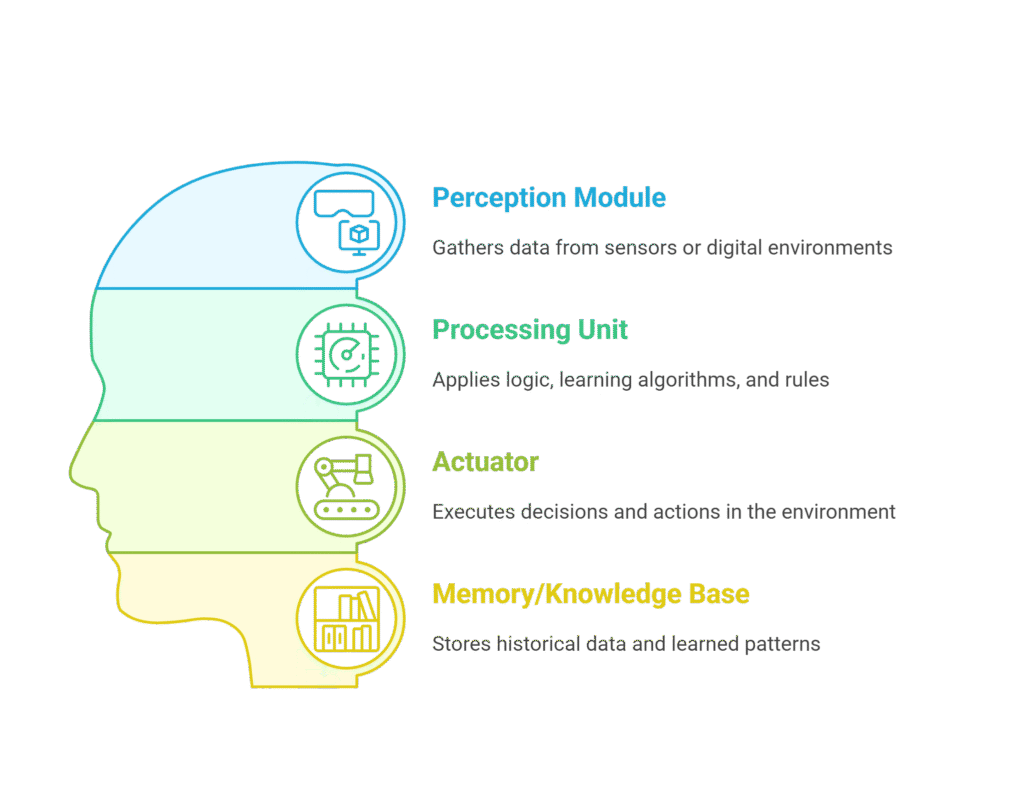
Key Components of AI Agents:
- Perception Module: Gathers data from sensors or digital environments.
- Processing Unit: Applies logic, learning algorithms, and rules.
- Actuator: Executes decisions and actions in the environment.
- Memory/Knowledge Base: Stores historical data and learned patterns.

The Evolution of AI Agents
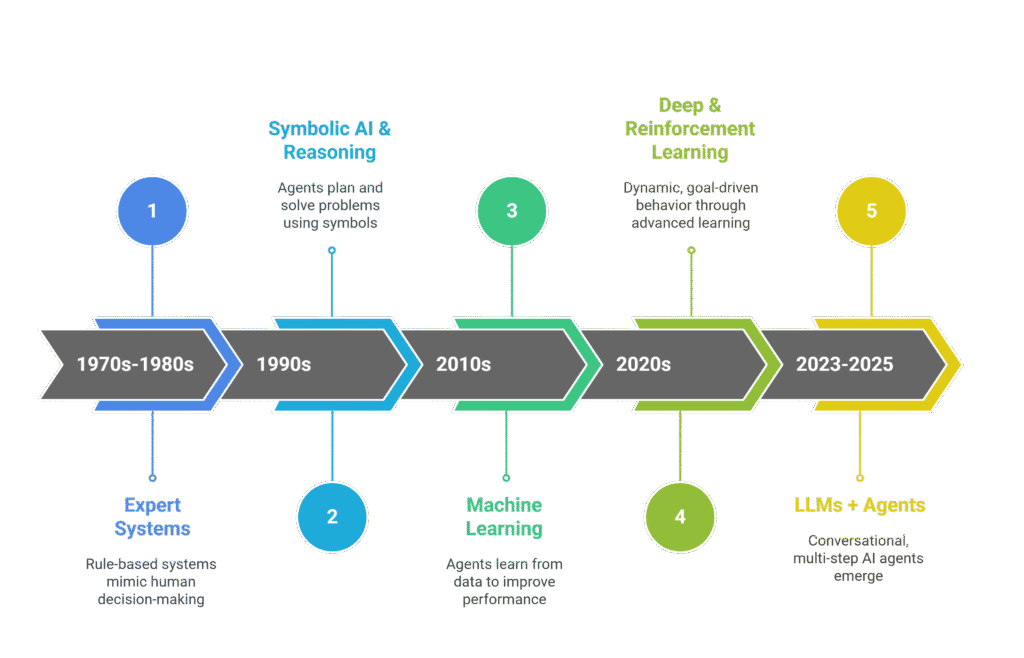
AI agents didn’t appear overnight. Their development is the culmination of decades of progress in AI subfields:
- Expert Systems (1970s-1980s): Rule-based systems that mimicked human decision-making.
- Symbolic AI and Reasoning Engines (1990s): Gave rise to agents that could plan and problem-solve.
- Machine Learning Revolution (2010s): Enabled agents to learn from data.
- Deep Learning & Reinforcement Learning (2020s): Allowed for dynamic, goal-driven behavior in agents.
- LLMs + Agents (2023-2025): Integration of large language models (LLMs) like GPT and Claude into agent frameworks created conversational, multi-step AI agents.

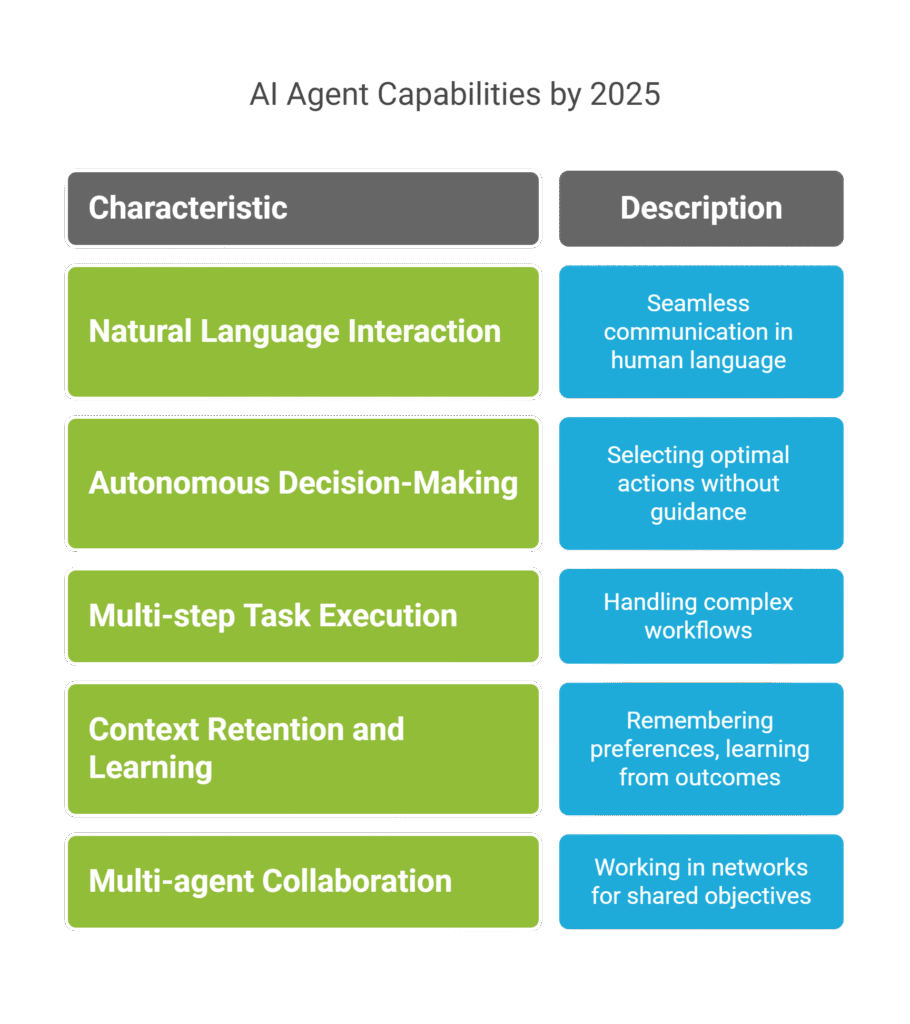
Core Capabilities of Modern AI Agents
By 2025, AI agents are capable of:
- Natural Language Interaction: Seamless communication in human language.
- Autonomous Decision-Making: Selecting optimal actions without human guidance.
- Multi-step Task Execution: Handling complex workflows (e.g., research, data analysis, reporting).
- Context Retention and Learning: Remembering user preferences, learning from outcomes.
- Multi-agent Collaboration: Working in networks with other agents to achieve shared objectives.

Real-World Applications in 2025
1. Business Process Automation
- Sales Agents: Tools like ChatGPT-powered agents now handle outreach, follow-ups, and CRM updates autonomously.
- Finance Bots: AI agents monitor expenses, manage budgets, and even execute investment strategies.
- Project Management Assistants: Schedule meetings, assign tasks, track progress, and summarize outcomes.
2. Healthcare and Medicine
- Clinical Support Agents: AI agents support doctors by analyzing symptoms, reviewing patient histories, and suggesting diagnoses.
- Medication Management: Personalized agents help patients track prescriptions, doses, and appointments.
- Mental Health Companions: Empathetic conversational agents like Woebot provide therapy support.
3. Education and Learning
- Personal Tutors: AI agents offer personalized tutoring based on student performance and learning style.
- Admin Support for Educators: Automate grading, curriculum planning, and feedback.
- Course Builders: Agents create customized learning paths and materials from vast online resources.
4. Software Development and IT
- Coding Agents: Tools like Devin (an autonomous software engineer) write, debug, and test code.
- Infrastructure Monitoring: Agents detect server anomalies, reroute traffic, and auto-heal infrastructure.
- Customer IT Support: LLM-powered agents resolve tickets, escalate issues, and improve over time.
5. Personal Productivity
- Email and Calendar Assistants: AI agents summarize, respond, and schedule efficiently.
- Daily Planners: Create and optimize to-do lists based on deadlines and habits.
- Personal Finance Managers: Track spending, make suggestions, and automate savings.
Industry Use Cases and Case Studies
a. Legal Sector: Harvey AI
Harvey is a legal AI agent trained on large sets of legal data. Deployed by major firms, it drafts contracts, reviews case files, and answers complex legal queries in seconds.
b. Customer Service: Klarna’s AI Agent
In 2024, Klarna replaced 700 customer service agents with a custom LLM agent that resolved over 2.3 million queries in its first month—at higher customer satisfaction rates.
c. Engineering & Design: Autodesk Dreamcatcher
AI agents assist in generative design by exploring thousands of design variations for optimal performance, saving weeks of human effort.
d. Marketing: Jasper & Copilot AI
Modern marketers use AI agents to analyze trends, generate content, run campaigns, and track KPIs.
The AI Agent Stack: Technologies Behind the Curtain
AI agents rely on a layered technology stack:
- Foundational Models: GPT-4/5, Claude, Gemini, etc.
- Prompt Engineering & Memory Layers: Vector databases (e.g., Pinecone), context retention modules.
- Execution Engines: LangChain, Auto-GPT, OpenAgents.
- Tool Use Integration: Browser plugins, APIs, code execution tools.
- Orchestration Frameworks: CrewAI, MetaGPT, AgentOps.
This stack enables agents to:
- Understand complex instructions.
- Break tasks into sub-tasks.
- Decide when and how to use external tools.
- Collaborate with other agents or humans.
Ethical, Legal, and Social Implications
As AI agents become more autonomous, important concerns arise:
- Data Privacy: Agents must handle sensitive data securely.
- Bias and Fairness: Decisions made by agents can reflect training data biases.
- Accountability: Who is responsible when an agent makes a mistake?
- Job Displacement: Routine roles are increasingly automated.
- Human Oversight: Balancing autonomy with control remains critical.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their promise, AI agents still face limitations:
- Context Limitations: Agents still struggle with long-term memory.
- Reasoning Gaps: Complex logic and abstract thinking are imperfect.
- Tool Fragility: Dependencies on APIs and services can break workflows.
- Security Risks: Agents with execution capabilities pose cybersecurity challenges.
The Future of AI Agents
Looking ahead, AI agents will:
- Evolve from Assistants to Colleagues: Sharing responsibilities and offering high-level strategic input.
- Gain Emotional Intelligence: Better understand tone, mood, and social context.
- Run Micro-enterprises: Fully autonomous agents managing online businesses, investments, and service delivery.
- Operate in Swarms: Coordinated agents solving problems at scale, from disaster response to planetary exploration.
Final Thoughts: A New Era of Digital Companionship
AI agents in 2025 mark a new chapter in human-computer interaction. They are not merely tools but collaborators, capable of independent action, complex problem-solving, and continuous learning.
As we move deeper into this era, businesses, creators, educators, and everyday users will need to embrace a new mindset—one that sees AI agents not as replacements, but as extensions of our human capabilities. The key to thriving in this future lies in learning to work with these agents, leveraging their strengths while preserving human creativity, judgment, and empathy.
The future isn’t coming. It’s already here. And it speaks, plans, and acts—in the voice of an AI agent. Take your first step and enroll in our free course: Automate Your First Workflow in 30 Minutes